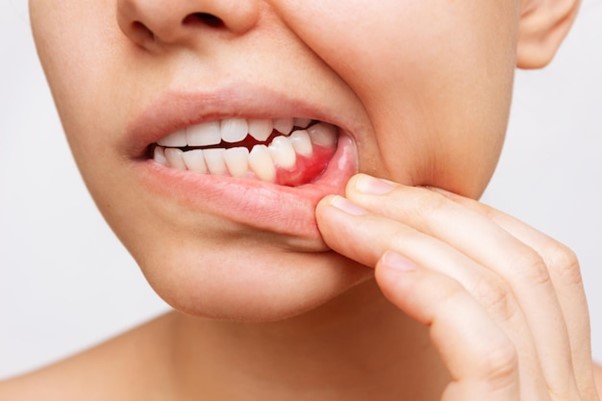
What Is Gum Disease?
Periodontal disease is an infection of the tissues that surround and support the teeth. It starts with gum inflammation (gingivitis) and can progress to periodontitis if not properly managed. Gingivitis causes swollen, red gums that may bleed easily. As the condition worsens into periodontitis, the infection can destroy the bones that hold the teeth in place, leading to lose teeth or tooth loss.
What are the Causes of Gum Disease?
Several factors contribute to the development of periodontal disease, including:
Poor oral hygiene: Not brushing and flossing regularly allows plaque to build up on the teeth, leading to gum inflammation.
Smoking or tobacco use: Tobacco products are a major risk factor for gum disease.
Diabetes: Uncontrolled blood sugar levels increase the risk of infections, including periodontal disease.
Hormonal changes: Pregnancy, menopause, and other hormonal shifts can make gums more sensitive and prone to inflammation.
Genetics: Some individuals may be more genetically predisposed to gum disease.
What are the Symptoms of Gum Disease?
Recognizing the signs of Gum disease early can help prevent its progression. Common symptoms include:
- Red, swollen, or bleeding gums
- Continuous bad breath
- Receding gums
- Loose or shifting teeth
- Painful chewing
If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s important to see your dentist for a check-up right away
How Can I Prevent Gum Disease?
The good news is that Gum disease is preventable with proper care. Here are some essential steps:
- Brush twice a day: Use fluoride toothpaste to remove plaque and prevent gum disease.
- Floss daily: Cleaning between your teeth helps remove food particles and plaque that brushing can miss.
- Quit smoking: Tobacco use significantly increases your risk of developing periodontal disease.
- Regular dental check-ups: Visiting your dentist twice a year can help detect and treat gum issues early.
- Manage health conditions: Controlling diabetes and other health issues can reduce your risk of gum infections.
How is Gum Disease Treated?
If Gum disease develops, your dentist can offer treatments to manage the condition. These may include:
- Scaling and root planing: A deep-cleaning procedure to remove plaque and tartar from below the gumline.
- Antibiotics: In some cases, antibiotics may be prescribed to reduce infection and inflammation.
- Surgery: Advanced cases may require surgery to restore gum health and prevent tooth loss.
Gum disease is a serious condition that can lead to tooth loss if left untreated. However, with good oral hygiene and regular dental care, it is entirely preventable. Recognizing early signs, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and seeing your dentist regularly can keep your gums healthy.
Don’t wait until it’s too late—schedule your dental check-up today to prevent or treat periodontal disease!